Creating Accessible Content in Loyalty
Loyalty allows marketers to create accessible content for different types of platform objects, such as Offers, Rewards, and Challenges. In many cases, this content is displayed to Members via a website or branded app.
When discussing the accessibility features of the Loyalty platform, it's important to understand a few key features of the platform's content management system.
Content in Loyalty is managed by means of a Template Set. A Template Set is an HTML document that controls what layouts, styles, and content elements are available to the marketer when they are creating content for an object that uses the Template Set. Loyalty supports a default Template Set for each platform object, but these Template Sets can also be modified to meet your specific business requirements. In most cases, the Template Set is defined as part of your Loyalty implementation. Any changes that need to be made to a Template Set are typically made by a technical resource, or by your Zeta Global team, by uploading a new HTML document into the platform.
A Template Set contains the necessary HTML code to describe one or more Layouts. A Layout represents a specific context in which content is displayed to a Member, such as a website, mobile device, or email message, for example. A Layout defines the size and shape of the content, as well as its formatting and visual appearance, and other interface elements, such as buttons or images.
The marketer end-user does not work directly with the raw HTML found in the Template Set, but instead creates or edit content for the object from the Content Editor screen, which is available on each object from the Display tab. The Content Editor presents all of the Layouts from the Template Set in a user-friendly interface designed for a non-technical end-user. Using the Content Editor, the marketer can build the content for an object without knowing how to code in HTML.
The features described below support the creation of accessible content, and are available to users, either from the Content Editor, or within the HTML that defines a Template Set.
Text Alternatives
You may be required to provide text alternatives to any non-text content, such as images. Loyalty supports text alternatives through alt tags, custom web fonts to match branding, and HTML buttons.
An alt tag, or alternative text, is a brief textual description of an image. The use of alt tags is supported directly in the Content Editor. Within a Layout, click an image to select it. From the contextual pop-up menu, click the Alternative Text icon to enter an alt tag.
You may be using image-based content because your on-brand fonts are not standard in browsers. You can use custom web fonts in Loyalty to stay on-brand, rather than using text in an image. Custom fonts are not supported in the Content Editor screen, but they can be included in the native HTML that defines a Template Set.
You may be using images for buttons. You can instead create accessible HTML-based buttons, and style them as needed. These types of buttons created via code instead of images are commonly referred to as “Bulletproof buttons.” Bulletproof buttons are not supported in the Content Editor screen, but they can be included in the native HTML that defines a Template Set.
Content Structure
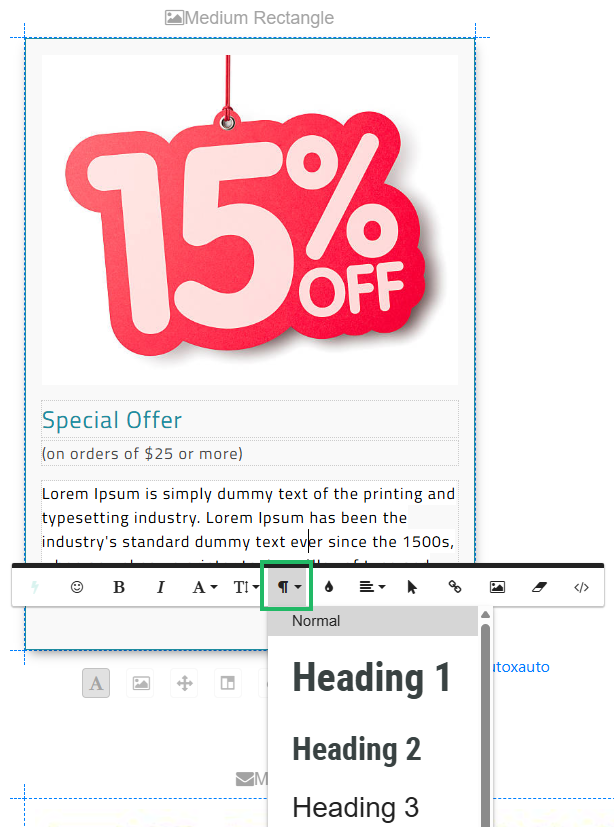
Some accessibility rules may require content objects to maintain logically organized content structure, with properly nested headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.). Heading styles are preferred for accessibility over relying solely on font size to convey the content structure.
The Content Editor screen allows you to apply heading styles to text blocks. Within a Layout, click a text block to select it. From the contextual pop-up menu, click the Paragraph Format icon to apply a heading style.
Accessible Tables
You can create tables in Loyalty that follow the ARIA Grid pattern for accessibility (click here to learn more about the ARIA Grid pattern). You can also set the tab order on forms. In addition, you can implement Semantic Markup, which uses tags on HTML elements according to their meaning and purposes, and not just their visual formatting. These features are not supported in the Content Editor screen, but they can be included in the native HTML that defines a Template Set.
Contrasting Colors
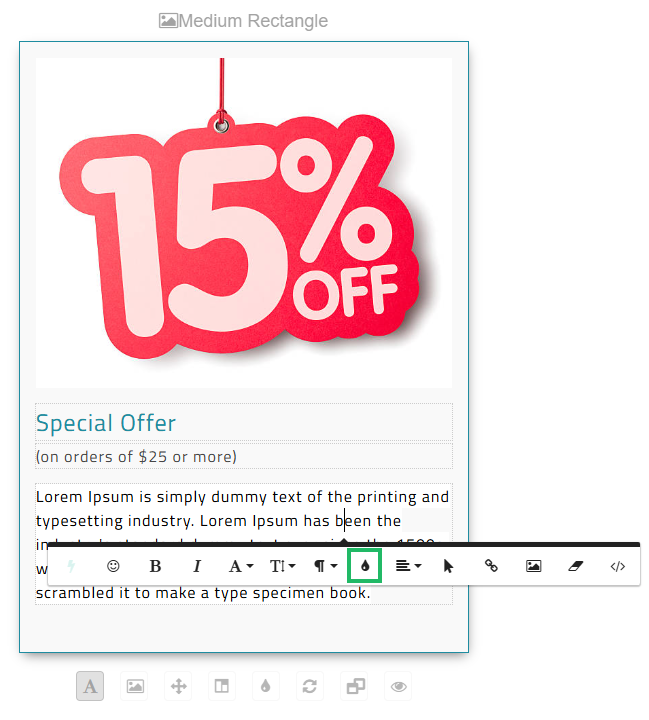
Creating content with strong contrast between text color and background color makes the text easier to read for people with low vision or color blindness. The Content Editor screen provides full control over the text and background colors, allowing you to create content with suitable contrast. Within a Layout, click a text block, then select the desired text within the block. From the contextual pop-up menu, click the Colors icon, then select either Text or Background, and enter the hex value for the desired color.